Viruses, Worms to Ransomware: What Are the Differences and How You Can Protect Yourself?
2021-11-11 09:21

Viruses, Worms and Trojans: What Are the Differences and How You Can Protect Yourself- by exali
Have you checked your smartphone today? Already booted up the PC? Whether at work or in your free time, everything requires a computer these days. So it’s all the more important that the systems and data are secured against external attacks. That’s reason enough to take a closer look at the dangers. We explain the difference between viruses, worms and the other virtual pests as well as the options available to protect yourself from them.
Types of Malware: An Overview
The term “malware” is made up of the words malicious and software and is more or less self-explanatory. Malware is a program that performs malicious functions and is designed to access a device without the user’s knowledge in order to compromise it. The terms malware, malicious program, badware, evilware or junkware are also frequently used. All of these applications have the same target: Your data. Depending on the malware, the data may be deleted, blocked, modified or copied. In addition, they put a strain on the computing power of your system. We introduce you to the best-known types of malware in the following.
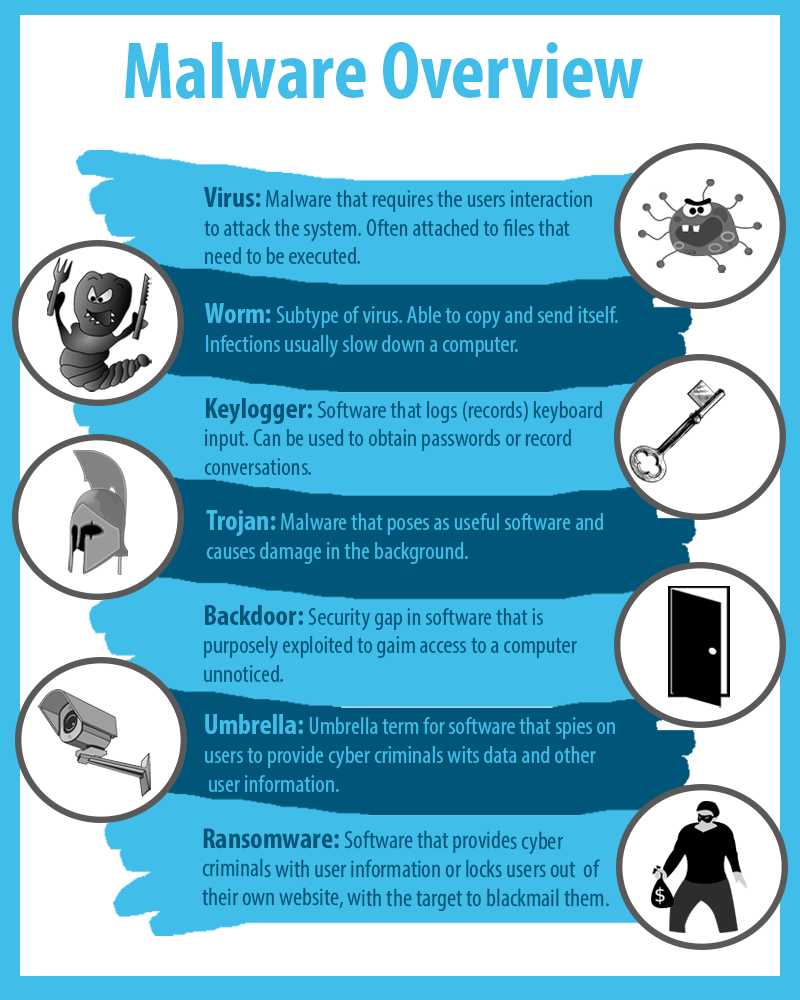
Backdoor, Spyware, Malware: The Difference Isn’t so Easy to Explain
Distinguishing the terms from one another is not that easy. For example, backdoors are often installed by programs that a Trojan horse has smuggled onto a system. And of course, spyware can be easily executed via the backdoor. Most users hardly see the difference between the various threats and generally refer to all malware as a computer virus. But, for the affected system, it doesn’t really matter which malicious program caused the damage. That’s because digital infections are like analog ones: As soon as they’re treated properly and you see improvement, it doesn’t really matter what strain of bacteria caused the disease. Or have you actually wondered what strain of bacteria made you sick after you recovered from a cold?
What Motivates Malware Programmers?
While your antivirus software is checking your computer, you may have asked yourself why some people program computer viruses or hack other computers in the first place. Malware programmers are usually quite intelligent and love challenges. In an interview with digitalwelt.org, one virus programmer said he did it because he was under-challenged, bored, wanted respect, and wanted to “show people”. Cyber criminals also share some motives with analog criminals. They want to experience a feeling of power, and since data is the gold of the digital age, they also steal euros or Bitcoin. According to a Federal Report, the average damage from computer fraud in Germany in 2017, as in 2016, was 4.000 euros.
How Can I Protect Myself from an Attack?
The only way to be 100 percent protected from malware is not to use a computer. So if you want to lead a life with a laptop, smartphone and navigation system, you have to learn to deal with a certain level of risk. The few things that can prevent malware damage are:
- Good anti-virus software: Some software is even available for free.
- System-wide antivirus scans
- Regular system updates (to close security gaps instantly)
- Being careful when handling emails and downloading programs
- Not using an administrator account in everyday life (this makes system-wide changes by malware more difficult)
- Being careful when exchanging data (regardless of whether it is a picture, video, music or game, everything can be affected)
- Creating backups of your data so you don’t end up empty-handed in the event of an attack
In addition, it is important to make sure you only use a single antivirus software; otherwise, important protective functions of different programs could cancel each other out.
If You’ve Already Been Infected: IT Forensic Scientists and the Question of Costs
Fortunately, the tips above help against all types of malware. However, once the damage has already been done, it can get really expensive. If your data is gone, if you have been locked out of the system or if the network is no longer accessible, costs can accrue. As an example calculation, let’s take an online shop that is unavailable for one day: The in-house IT team works overtime (approx. 13.000 euros), specialists come to the company (costs for IT forensics: 19.500 euros), lost sales (100.000 euros), bad reviews from customers (marketing damage / image damage 17.500 euros). This adds up to 150.000 euros. A hefty sum that will be even higher if you don’t react immediately. The replacement of the lost data also hasn’t been included here.
Protection with Professional Indemnity
You should think about the right protection in good time so you aren’t stuck with the costs. Here’s something a lot of people don’t know: You can get insurance against cyber damage and hacker attacks! There are two ways to do this at exali:
- Professional Indemnity Insurance through exali has integrated coverage for data and cyber damage that you may cause to third parties through a mistake (for example, if customer data is stolen during a hacker attack).
- With the First-party Cyber and Data Risks Insurance (FPC) add-on, you can flexibly “upgrade” all professional indemnity insurance from exali so your own business is optimally protected in the event of a cyber attack. For example, the insurance company will then cover the costs of restoring your IT systems.